Kaspa: A Comprehensive Guide to the BlockDAG Cryptocurrency
Introduction
Kaspa is an innovative Layer 1 blockchain that combines the security of Bitcoin's Proof of Work (PoW) consensus with a novel BlockDAG architecture. This guide will explore Kaspa's unique features, its operating principles, and how to mine KAS tokens. Whether you're a crypto enthusiast or a potential miner, this article will provide valuable insights into this cutting-edge blockchain technology.
Table of Contents
What is Kaspa?
Kaspa is a Layer 1 blockchain that uses a Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, similar to Bitcoin. However, Kaspa distinguishes itself by employing a BlockDAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) architecture instead of a traditional linear blockchain. This innovative structure allows for parallel block generation, significantly improving transaction speed and network throughput.
Kaspa Team Background
The Kaspa project was initially proposed in 2018 by Yonatan Sompolinsky and Aviv Zohar, the same scholars who introduced the GHOST (Greedy Heaviest-Observed Sub-Tree) protocol, which later became part of Ethereum's consensus mechanism.
Kaspa launched its testnet in 2020 to evaluate and optimize its BlockDAG technology and overall network performance. Following successful testnet operations, Kaspa officially launched its mainnet in 2021, marking its formal entry into the cryptocurrency market.
How Does Kaspa Work?
Structural Model: Directed Acyclic Graph
Kaspa introduces the PHANTOM protocol, a permissionless ledger protocol based on Proof of Work that extends Satoshi Nakamoto's blockchain concept to a Directed Acyclic Graph (BlockDAG). PHANTOM can reference multiple previous blocks, providing a total ordering of all blocks and transactions while outputting a consistent set of accepted transactions.
The PHANTOM protocol includes a parameter 'k' that controls the protocol's tolerance for simultaneously created blocks, allowing for higher throughput. When k=0, it represents a single-chain, longest-chain structure like Bitcoin.
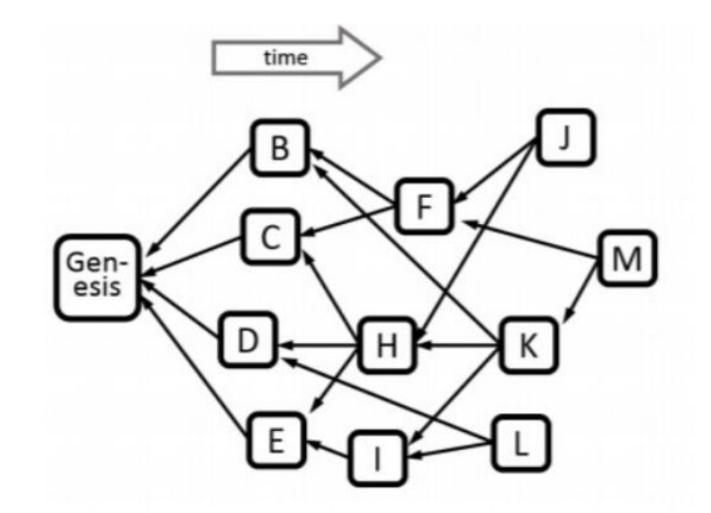
Identifying Honest and Malicious Blocks
PHANTOM addresses the challenge of distinguishing between honest and malicious blocks. Malicious attacks are characterized by low connectivity between blocks generated by malicious nodes and those generated by honest nodes, while connectivity among honest nodes' blocks is typically higher.
The parameter 'k' serves as the criterion for this judgment. For a specific block X, if the intersection of anticone(X) with honest blocks exceeds k, it indicates low connectivity between X and honest blocks, and X is classified as an attack block. Conversely, high connectivity suggests X is an honest block.
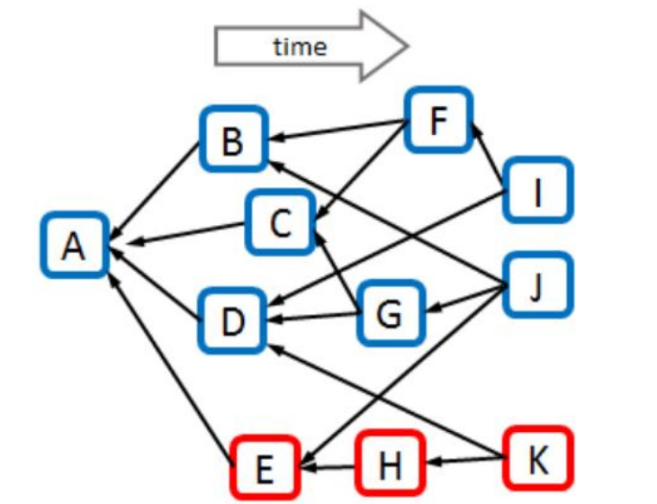
Linear Ordering
The GHOSTDAG protocol resolves the double-spending problem by scoring each block based on its connectivity (the number of elements in its past block set). The block with the highest total score forms the main chain, creating the initial subset. Remaining blocks vote sequentially according to the main chain order, resulting in a network-wide vote trending from high to low connectivity.
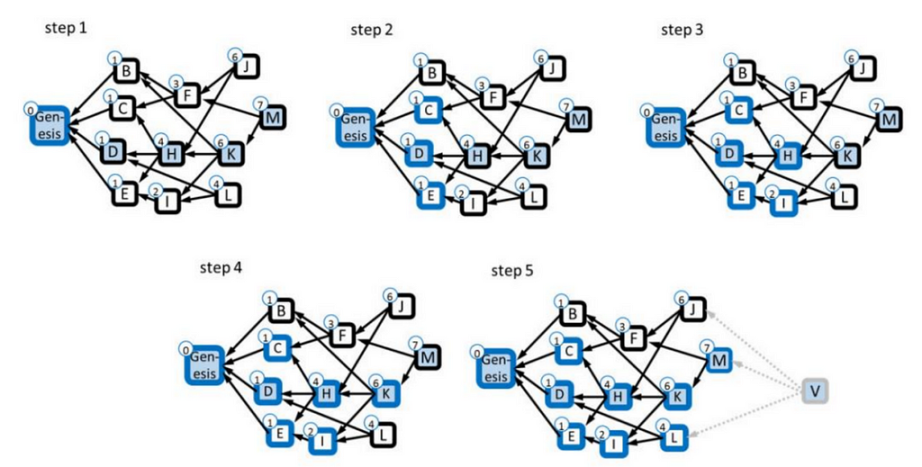
Understanding KAS Tokens
KAS is Kaspa's native network token. Similar to Bitcoin, KAS has no pre-mining or pre-sale activities, with all tokens obtainable only through mining, ensuring 100% decentralization.
KAS Tokenomics
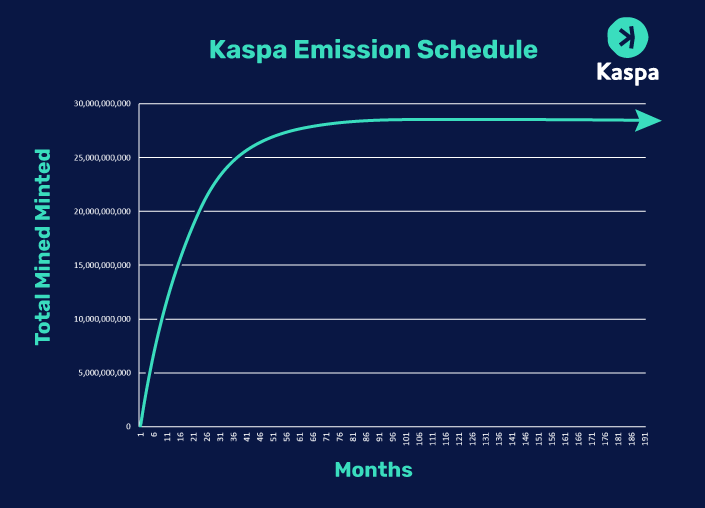
Kaspa has a maximum supply of 28.7 billion tokens, to be mined within 186 months. It follows a deflationary monetary policy:
- In the first six months after mainnet launch, 500 KAS are generated per second, totaling 1,314,900,000 KAS monthly.
- From the seventh month, the monthly KAS supply decreases by 12%.
- Subsequent monthly emissions are calculated as the previous month's KAS emission * (1/2)^(1/12), effectively halving the total supply annually.
KAS Token Performance
KAS tokens are listed on several centralized exchanges, including Bybit, Bitget, and Kucoin. Binance has also launched KAS perpetual contracts. As of writing, KAS is trading at $0.17, with a circulating supply of 24,072,216,304 KAS and a market cap of approximately $4.21 billion.
Kaspa Mining Guide
Kaspa uses the kHeavyHash mining algorithm, supporting GPU solo mining or dual mining with ETHW and ETC. It also supports some FPGA and ASIC miners. Note that ASIC miners currently dominate Kaspa mining, making it less profitable for GPU users. However, you can still use the following guide to experience decentralized mining:
Solo Mining Kaspa
- Run a Kaspa node
- Create a wallet
- Run the wallet daemon
- Check your balance
- Download and run mining software (e.g., tmrlvi gpu miner or kaspaminer.exe)
Dual Mining Kaspa
Both lolMiner and Bzminer support dual mining (NVIDIA and AMD) on Windows and Linux. When dual mining ETC+Kaspa, you'll need to provide wallets and pools for both Kaspa and the other token.
Using lolMiner as an example:
- Create a new file named
dual_mine_etc_kaspa.bat - Input the dual mining command, replacing ETH/ETC and Kaspa addresses with your own
- Save and double-click
dual_mine_etc_kaspa.batto start mining
By following this guide, you'll gain a comprehensive understanding of Kaspa's innovative blockchain technology and how to participate in its ecosystem through mining.
Keywords for SEO: Kaspa, BlockDAG, cryptocurrency, mining, KAS tokens, Proof of Work, blockchain technology, PHANTOM protocol, GHOSTDAG, decentralized mining, dual mining